
Give an Inch, Take a Foot Elementary School Activity
Students practice measuring techniques by measuring different objects and distances around the classroom. They practice using different scales of measurement in metric units and estimation. Also, students learn how measurement is used in engineering and why accuracy is important to the design of new products.

Designing Bridges Middle School Lesson
Students learn about the types of possible loads, how to calculate ultimate load combinations, and investigate the different sizes for the beams (girders) and columns (piers) of simple bridge design. They learn the steps that engineers use to design bridges by conducting their own hands on associated activity to prototype their own structure. Students will begin to understand the problem, and learn how to determine the potential bridge loads, calculate the highest possible load, and calculate the amount of material needed to resist the loads.

Biomimicry: Natural Designs Elementary School Activity
Students learn about biomimicry and how engineers often imitate nature in the design of innovative new products. They demonstrate their knowledge of biomimicry by practicing brainstorming and designing a new product based on what they know about animals and nature.

Engineering an Animal’s Survival Elementary School Activity
This unique engineering activity explores helping animals that cannot help themselves. Students perform research and design prosthetic prototypes for an animal to use for its survival. First, students choose an animal from a set of task cards. These cards have descriptions of animals that have injuries that keep them from getting what they need in the wild. Next, students work in pairs to research these animals and their habitats. They then create habitats for their animals to live and model 3D prosthetics for the animals to use with modeling clay. Finally, students share their habitats with their peers.

Pill Dissolving Demo High School Activity
In a class demonstration, the teacher places different pill types ("chalk" pill, gel pill, and gel tablet) into separate glass beakers of vinegar, representing human stomach acid. After 20-30 minutes, the pills dissolve. Students observe which dissolve the fastest, and discuss the remnants of the various pills. What they learn contributes to their ongoing objective to answer the challenge question presented in lesson 1 of this unit.

Three-Tower Types Challenge: Tower Investigation and the Egg Middle School Activity
Towers have been a part of developed society for centuries, serving a variety of purposes, from watch towers to modern cell towers. In this activity, student groups design and build three types of towers (guyed or cable-supported, free-standing or self-standing, and monopole), engineering them to meet the requirements that they hold an egg one foot high for 15 seconds.
Electricity and Magnetic Fields High School Lesson
The grand challenge for this legacy cycle unit is for students to design a way to help a recycler separate aluminum from steel scrap metal. In previous lessons, they looked at how magnetism might be utilized. In this lesson, students think about how they might use magnets and how they might confront the problem of turning off the magnetic field. Through the accompanying activity, students explore the nature of an electrically induced magnetic field and its applicability to the needed magnet for this design challenge.

How a Faucet Works Middle School Lesson
Students learn about the underlying engineering principals in the inner workings of a simple household object – the faucet. Students use the basic concepts of simple machines, force and fluid flow to describe the path of water through a simple faucet. Lastly, they translate this knowledge into thinking about how different designs of faucets also use these same concepts.

Doing the Math: Analysis of Forces in a Truss Bridge High School Lesson
In this lesson, students learn the basics of the analysis of forces engineers perform at the truss joints to calculate the strength of a truss bridge. This method is known as the “method of joints.” Finding the tensions and compressions using this method will be necessary to solve systems of linear equations where the size depends on the number of elements and nodes in the truss. The method of joints is the core of a graphic interface created by the author in Google Sheets that students can use to estimate the tensions-compressions on the truss elements under given loads, as well as the maximum load a wood truss structure may hold (depending on the specific wood the truss is made of) and the thickness of its elements.
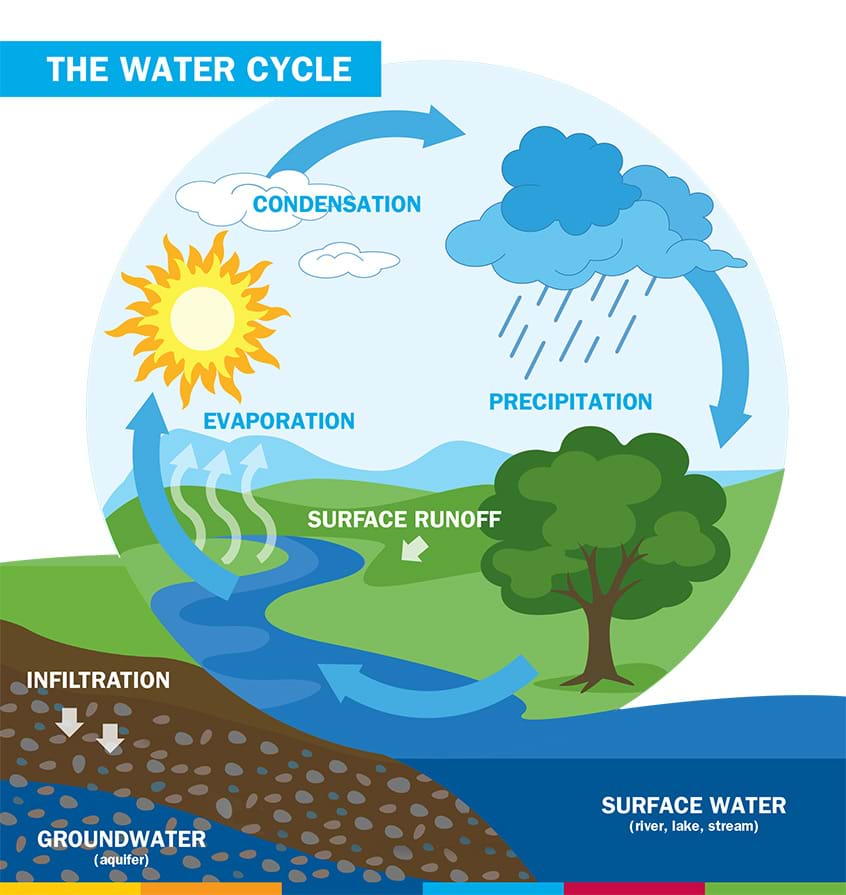
Water Cycle Elementary School CurricularUnit
Water is essential to life. Understanding how the water cycle works, the importance of water as a natural resource, and how our household water cycle functions is essential knowledge for everyone. Through a range of water-based explorations and the engineering design process, students learn about the water cycle and how engineers manage it.

Spaghetti Bridges Middle School Activity
Civil engineers design structures such as buildings, dams, highways and bridges. Student teams explore the field of engineering by making bridges using spaghetti as their primary building material. Then they test their bridges to see how much weight they can carry before breaking.

Design and Build a Rube Goldberg Middle School Activity
In this two-part activity, students design and build Rube Goldberg machines. This open-ended challenge employs the engineering design process and may have a pre-determined purpose, such as rolling a marble into a cup from a distance, or let students decide the purposes.

Saltwater Circuit Middle School Activity
Students build a saltwater circuit, which is an electrical circuit that uses saltwater as part of the circuit. Students investigate the conductivity of saltwater, and develop an understanding of how the amount of salt in a solution impacts how much electrical current flows through the circuit. They learn about one real-world application of a saltwater circuit — as a desalination plant tool to test for the removal of salt from ocean water.

Design a Parachute Middle School Activity
After a discussion about what a parachute is and how it works, students create parachutes using different materials that they think will work best. They test their designs, and then contribute to a class discussion (and possible journal writing) to report which paper materials worked best.

Water Bottle Rockets Middle School Activity
What makes rockets fly straight? What makes rockets fly far? Why use water to make the rocket fly? Students are challenged to design and build rockets from two-liter plastic soda bottles that travel as far and straight as possible or stay aloft as long as possible. Guided by the steps of the engineering design process, students first watch a video that shows rocket launch failures and then participate in three teacher-led mini-activities with demos to explore key rocket design concepts: center of drag, center of mass, and momentum and impulse. Then the class tests four combinations of propellants (air, water) and center of mass (weight added fore or aft) to see how these variables affect rocket distance and hang time. From what they learn, student pairs create their own rockets from plastic bottles with cardboard fins and their choices of propellant and center of mass placement, which they test and refine before a culminating engineering field day competition. Teams design for maximum distance or hang time; adding a parachute is optional. Students learn that engineering failures during design and testing are just steps along the way to success.
Last updated 24 hour(s) ago

