Space
The ongoing deep dive into outer space pushes engineers to work together to innovate products and machines that are out of this world!
Exploration into space and neighboring planets has resulted in many awe-inspiring engineering feats—like Armstrong’s moon landing, the launches of the 16 Mars Landers and 5 sub-landers, the design and maintenance of the International Space Station and more!
Human space exploration allows engineers and scientists to dig into fundamental questions about the history of the solar system and the various phenomena of space, pushing boundaries on new technologies and creating new industries.
It takes multidisciplinary teams with various experiences and viewpoints to peer into the unknown, unravel the secrets of the universe and make sense of space phenomena! Space travel is made possible by many different types of engineers — including the aerospace engineers who design, model and test the spacecraft, the mechanical engineers who design and create the hardware components, and the electrical and computer engineers who design the systems controlling the transportation and automation of the spacecraft and satellites.
And, more types of engineers contribute their unique skills and knowledge: chemical engineers design and optimize the rocket fuel to maximize the spacecraft launch and minimize the environmental impacts while biomedical engineers design methods and devices to keep astronauts’ healthy while traveling in space.
Engineers of all disciplines shape the past, current and future explorations into space.
Space Curricula
Grades K-2
- Coming Soon!
Grades 3-5
- Spaced OutSpaced Out

Students are introduced to the space environment, learning about the major differences between the environment on Earth and that of outer space (atmosphere, radiation, microgravity)— and the engineering challenges that arise because of these differences. To prepare students for the upcoming lessons ...
- Space ShelterSpace Shelter

Students are given the following engineering challenge: "The invasion has taken place and we need to find a new home. To ensure your survival beyond Earth's occupation you must design a shelter that can be built on another planet."
- Using Thrust, Weight & Control: Rocket Me into SpaceUsing Thrust, Weight & Control: Rocket Me into Space

Through the continuing storyline of the Rockets unit, this lesson looks more closely at Spaceman Rohan, Spacewoman Tess, their daughter Maya, and their challenges with getting to space, setting up satellites, and exploring uncharted waters via a canoe. Students are introduced to the ideas of thrust,...
- Spacecraft Design: Beat the HeatSpacecraft Design: Beat the Heat

To understand the challenges of satellite construction, student teams design and create model spacecraft to protect vital components from the harsh conditions found on Mercury and Venus. They use slices of butter in plastic eggs to represent the internal data collection components of the spacecraft....
- Life in Space: The International Space StationLife in Space: The International Space Station

Students are introduced to the International Space Station (ISS) with information about its structure, operation and key experiments.
- See More
Grades 6-8
- Robots on Ice Engineering ChallengeRobots on Ice Engineering Challenge

In a simulation of potential future space missions to Europa, one of Jupiter’s moons, student teams are challenged to direct a robot placed in an enclosed maze to search for and find the most “alien life.” The student teams compete as if they are space agencies creating their own exploratory systems...
- The Great Gravity EscapeThe Great Gravity Escape

Students use water balloons and a length of string to understand how the force of gravity between two objects and the velocity of a spacecraft can balance to form an orbit. They see that when the velocity becomes too great for gravity to hold the spacecraft in orbit, the object escapes the orbit and...
- My Moon ColonyMy Moon Colony

Students are introduced to the futuristic concept of the moon as a place people can inhabit. They brainstorm what people would need to live on the moon and then design a fantastic Moon colony and decide how to power it. Students use the engineering design process, which includes researching various ...
- AsteroidsAsteroids

Students learn some basic facts about asteroids in our solar system, mainly about the size of asteroids and how that relates to the potential danger of an asteroid colliding with the Earth. Students are briefly introduced to the destruction that would ensue should a large asteroid hit, as it did 65 ...
- An Inflated Impression of MarsAn Inflated Impression of Mars
Students use scaling from real-world data to obtain an idea of the immense size of Mars in relation to the Earth and the Moon, as well as the distances between them. Students calculate dimensions of the scaled versions of the planets, and then use balloons to represent their relative sizes and locat...
- See More
Grades 9-12
- Shielding from Cosmic Radiation: Space Agency ScenarioShielding from Cosmic Radiation: Space Agency Scenario
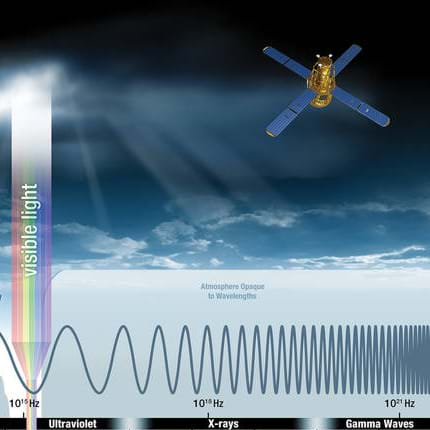
Through role playing and problem solving, this lesson sets the stage for a friendly competition between groups to design and build a shielding device to protect humans traveling in space. The instructor asks students—how might we design radiation shielding for space travel?