Quick Look
Grade Level: 10 (9-11)
Time Required: 1 hour
Expendable Cost/Group: US $7.00
Group Size: 3
Activity Dependency: None
Subject Areas: Physical Science, Physics
NGSS Performance Expectations:

| HS-PS3-1 |

Summary
In this hands-on activity—rolling a ball down an incline and having it collide into a cup—the concepts of mechanical energy, work and power, momentum, and friction are all demonstrated. During the activity, students take measurements and use equations that describe these energy of motion concepts to calculate unknown variables and review the relationships between these concepts.Engineering Connection
Light rail trains are a modern form of public transportation powered by overhead electrical lines that travel along a dedicated pathway of steel rails. To design these trains to be quiet, efficient and safe, engineers considere all of the energy of motion concepts: the work required to convert the mechanical energy when the train goes from a stopped position to forward/backward motion, how much momentum the train acquires between stations, and the power required to overcome the friction between the train's wheels and the effects of drag.
Learning Objectives
After this activity, students should be able to:
- Identify components of mechanical energy, work and power, momentum and friction and how they interrelate.
- Construct a model to demonstrate potential and kinetic energy, work, power, momentum and friction.
- Explain that energy, work and power, momentum and friction can be described by equations.
- Use multiple equations to solve for unknown variables.
Educational Standards
Each Teach Engineering lesson or activity is correlated to one or more K-12 science,
technology, engineering or math (STEM) educational standards.
All 100,000+ K-12 STEM standards covered in Teach Engineering are collected, maintained and packaged by the Achievement Standards Network (ASN),
a project of D2L (www.achievementstandards.org).
In the ASN, standards are hierarchically structured: first by source; e.g., by state; within source by type; e.g., science or mathematics;
within type by subtype, then by grade, etc.
Each Teach Engineering lesson or activity is correlated to one or more K-12 science, technology, engineering or math (STEM) educational standards.
All 100,000+ K-12 STEM standards covered in Teach Engineering are collected, maintained and packaged by the Achievement Standards Network (ASN), a project of D2L (www.achievementstandards.org).
In the ASN, standards are hierarchically structured: first by source; e.g., by state; within source by type; e.g., science or mathematics; within type by subtype, then by grade, etc.
NGSS: Next Generation Science Standards - Science
| NGSS Performance Expectation | ||
|---|---|---|
|
HS-PS3-1. Create a computational model to calculate the change in the energy of one component in a system when the change in energy of the other component(s) and energy flows in and out of the system are known. (Grades 9 - 12) Do you agree with this alignment? |
||
| Click to view other curriculum aligned to this Performance Expectation | ||
| This activity focuses on the following Three Dimensional Learning aspects of NGSS: | ||
| Science & Engineering Practices | Disciplinary Core Ideas | Crosscutting Concepts |
| Create a computational model or simulation of a phenomenon, designed device, process, or system. Alignment agreement: | Energy is a quantitative property of a system that depends on the motion and interactions of matter and radiation within that system. That there is a single quantity called energy is due to the fact that a system's total energy is conserved, even as, within the system, energy is continually transferred from one object to another and between its various possible forms. Alignment agreement: Conservation of energy means that the total change of energy in any system is always equal to the total energy transferred into or out of the system.Alignment agreement: Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can be transported from one place to another and transferred between systems.Alignment agreement: Mathematical expressions, which quantify how the stored energy in a system depends on its configuration (e.g. relative positions of charged particles, compression of a spring) and how kinetic energy depends on mass and speed, allow the concept of conservation of energy to be used to predict and describe system behavior.Alignment agreement: The availability of energy limits what can occur in any system.Alignment agreement: | Models can be used to predict the behavior of a system, but these predictions have limited precision and reliability due to the assumptions and approximations inherent in models. Alignment agreement: Science assumes the universe is a vast single system in which basic laws are consistent.Alignment agreement: |
Common Core State Standards - Math
-
Model with mathematics.
(Grades
K -
12)
More Details
Do you agree with this alignment?
-
Reason abstractly and quantitatively.
(Grades
K -
12)
More Details
Do you agree with this alignment?
-
Solve linear equations and inequalities in one variable, including equations with coefficients represented by letters.
(Grades
9 -
12)
More Details
Do you agree with this alignment?
-
Rearrange formulas to highlight a quantity of interest, using the same reasoning as in solving equations.
(Grades
9 -
12)
More Details
Do you agree with this alignment?
-
Summarize, represent, and interpret data on a single count or measurement variable
(Grades
9 -
12)
More Details
Do you agree with this alignment?
-
Reason quantitatively and use units to solve problems.
(Grades
9 -
12)
More Details
Do you agree with this alignment?
International Technology and Engineering Educators Association - Technology
-
Energy cannot be created nor destroyed; however, it can be converted from one form to another.
(Grades
9 -
12)
More Details
Do you agree with this alignment?
State Standards
Colorado - Math
-
Solve linear equations and inequalities in one variable, including equations with coefficients represented by letters.
(Grades
9 -
12)
More Details
Do you agree with this alignment?
-
Use units as a way to understand problems and to guide the solution of multi-step problems.
(Grades
9 -
12)
More Details
Do you agree with this alignment?
-
Reason quantitatively and use units to solve problems.
(Grades
9 -
12)
More Details
Do you agree with this alignment?
-
Rearrange formulas to highlight a quantity of interest, using the same reasoning as in solving equations.
(Grades
9 -
12)
More Details
Do you agree with this alignment?
-
Summarize, represent, and interpret data on a single count or measurement variable.
(Grades
9 -
12)
More Details
Do you agree with this alignment?
Colorado - Science
-
Describe energy transformations both quantitatively and qualitatively
(Grades
9 -
12)
More Details
Do you agree with this alignment?
Materials List
Each group needs:
- yardstick (for the activity setup)
- metric ruler (for measuring distance)
- 4 dowel rods, 3-feet long, ¼-in thick
- golf ball (or similar-sized ball)
- plastic or Syrofoam cup (must be lightweight, not heavy)
- scale (to weigh the golf ball and cup)
- tape
- paper towel or 3-4 tissues
- Ramp and Review Worksheet
Worksheets and Attachments
Visit [www.teachengineering.org/activities/view/cub_energy_lesson05_activity2] to print or download.Introduction/Motivation
Picture yourself atop a big hill with a scooter. Do you know how much potential energy you have? How fast will you be going when you reach the bottom? How much momentum will you have at the bottom? If you press hard on your brakes and slide to a stop, how much work will friction have done? The following activity models this scenario and helps you answer these questions.
Procedure
Before the Activity
- Gather materials and make copies of the Ramp and Review Worksheet, one per group.
- (optional) Set up a demo test station to help students visualize how the pieces go together.
With the Students
- Divide the class into teams of two to four students each. Hand out the materials to each group.
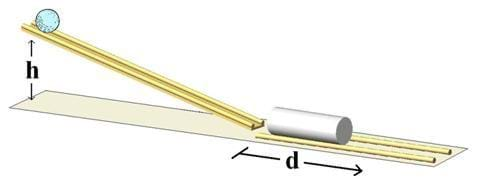
- Tape two dowel rods to each edge (of the same side) of a yardstick, approximately 1-inch apart from each other. This serves as a track for a golf ball to roll down.
- Prop the yardstick against a wall or desk or rest upon a large stack of books to create a slope for the ball to roll down.
- Place the cup at the end of the yardstick, and tape two dowel rods onto the table the width of the widest part of the cup. This serves as a track to ensure the cup travels in a straight path.
- Place a crushed paper towel or 3-4 tissues inside the bottom of the cup to absorb the impact of the ball and help keep the ball in the cup.
- Place the cup at the end of the yardstick ramp to catch the ball at the end of the incline.
- Record on your worksheet the mass of the ball and cup, as well as the height of the ramp.
- Place the ball at the top of the ramp, and let it go!
- Measure the distance the cup travels at the end of the ramp. Repeat this step three times and record the average value.
- Complete the Calculations and Results section of the worksheet.
- Keeping in mind your results, complete the Further Learning section of the worksheet.
Assessment
Pre-Activity Assessment
Brainstorming: Have students engage in open discussion. Remind them that no idea or suggestion is "silly." All ideas should be respectfully heard. Ask them to think of situations engineers face that involve a combination of mechanical energy, momentum, collisions, work and power, and friction. (Example answer: Designing a roller coaster or slide: potential energy turns into kinetic energy; friction from sliding: as you gain velocity, you gain momentum.)
Activity Embedded Assessment
Worksheet: Have students use the Ramp and Review Worksheet to record measurements and follow along with the activity. Encourage students to compare answers from the Further Learning section.
Hypothesize: Ask each group what would happen to the coefficient of friction if a heavier glass cup was used instead of a lightweight cup. (Answer: The coefficient of friction would be the same; however, the frictional force would increase.) Ask what would happen to the coefficient of friction if the surface was changed to ice. (Answer: The coefficient would decrease because less frictional force occurs on ice.)
Post-Activity Assessment
Worksheet Discussion: As a class, review and discuss worksheet answers from the Further Learning section. The answers reveal students' mastery of the concepts.
Discussion Questions: As a group, ask the following wrap-up questions. Have students raise their hands to answer. Write the answers on the classroom board.
- Why is work expressed as a negative value? (Answer: Work is defined as "force acting over a distance." When the force and distance traveled are in the same direction, the value of work is positive. However, in this case of friction, the force is acting in the opposite direction of the sliding cup; hence, a negative value of work.)
- How did the friction, momentum, kinetic and potential energy, and work and power all come together to make the cup move? How does this relate to activities you do every day? (Answer: To make the cup move, first we built up momentum by giving the ball potential energy and converting it into kinetic energy. When the ball reached the bottom of the track, it collided with the cup and conserved momentum. Once the cup started sliding, friction came into play to bring the cup to a stop. The power of friction was related to how fast the cup stopped. This is very similar to riding down a hill with a scooter, skateboard or bicycle and braking to a stop.)
Troubleshooting Tips
If the ball falls out of the cup,
- Adjust the slide rails so that the cup cannot turn while sliding.
- Place the cup on a smooth surface and not on carpet.
- If the yardstick is angled too high or too low, the cup will not slide as well as it could. Adjust the yardstick to approximately a 30˚–40˚ angle.
Make sure students are consistent and precise in their measurements. For example, when measuring how far the cup slid, measure from the front of the cup because the front of the cup started at the zero meter mark.
Activity Extensions
Another form of mechanical energy that has not been discussed in this unit is called rotational energy. In actuality, as the ball rolls down the incline, some of the potential energy is turned into rotational energy, while the rest is turned into kinetic energy. This decreases the ball's velocity as it rolls down the incline and makes our calculated value of velocity slightly higher than it really is. Assign students to search the Internet to find out more about rotational energy and why it causes certain objects to roll slower down inclines.
Activity Scaling
For younger students, conduct the middle school version of the activity, which includes a scaled-down worksheet.
If time is limited, assign the worksheet as homework.
Subscribe
Get the inside scoop on all things Teach Engineering such as new site features, curriculum updates, video releases, and more by signing up for our newsletter!More Curriculum Like This
In this hands-on activity—rolling a ball down an incline and having it collide into a cup—the concepts of mechanical energy, work and power, momentum, and friction are all demonstrated. During the activity, students take measurements and use equations that describe these energy of motion concepts to...
On the topic of energy related to motion, this summary lesson ties together the concepts introduced in the previous four lessons and show how the concepts are interconnected in everyday applications. A hands-on activity demonstrates this idea and reinforces students' math skills in calculating energ...
Learn the basics of the analysis of forces engineers perform at the truss joints to calculate the strength of a truss bridge known as the “method of joints.” Find the tensions and compressions to solve systems of linear equations where the size depends on the number of elements and nodes in the trus...
High school students learn how engineers mathematically design roller coaster paths using the approach that a curved path can be approximated by a sequence of many short inclines. They apply basic calculus and the work-energy theorem for non-conservative forces to quantify the friction along a curve...
Copyright
© 2007 by Regents of the University of ColoradoContributors
Chris Yakacki; Malinda Schaefer Zarske; Denise W. Carlson; Ben Sprague; Janet YowellSupporting Program
Integrated Teaching and Learning Program, College of Engineering, University of Colorado BoulderAcknowledgements
The contents of this digital library curriculum were developed under grants from the Fund for the Improvement of Postsecondary Education (FIPSE), U.S. Department of Education and the National Science Foundation (GK-12 grant no. 0338326). However, these contents do not necessarily represent the policies of the Department of Education or National Science Foundation, and you should not assume endorsement by the federal government.
Last modified: January 23, 2020






User Comments & Tips