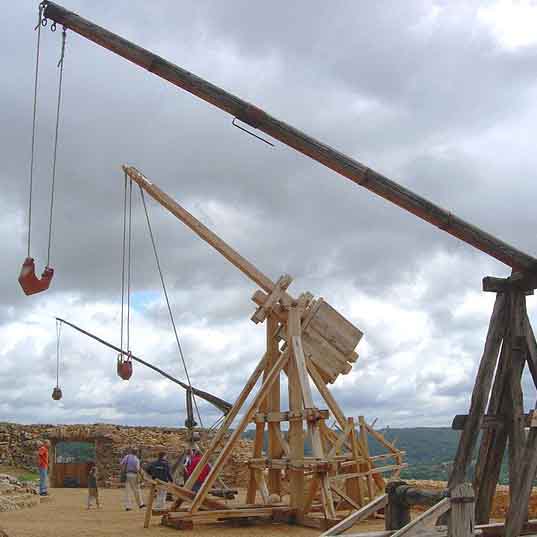
Simple Machines
Engineers use - and combine simple machines to design complex devices to make our lives easier!
Simple machines are basic devices that help accomplish physical tasks with few or no moving parts. The six most common simple machines – inclined plane, wedge, screw, lever, pulley and wheel-and-axle – are designed to change the magnitude/direction of the force (remember, work = force x distance), ultimately making the task easier to perform.
The six most common simple machines
A grooved circular disk (or disks) that guide a rope or cable pulled around its perimeter. With a single pulley engineers can change the direction of an applied force, such as pulling a rope down to lift a weight up. However, using a combination of pulleys in a pulley system can change both the amount and direction of the applied effort. Engineers design large machines, like cranes, bulldozers and elevators, with a system of pulleys to manipulate huge loads with a little force supplied by a relatively small motor.
An inclined plane that is wrapped around a cylinder. Engineers use screws in a variety of ways, including fasteners that are used to attach wood or metal; lifting screws that are used to lift heavy objects and dig holes; and bolts that are used with nuts to keep things together.
A long beam that rests on a point or support called a fulcrum. By positioning the fulcrum close to a heavy object and applying an effort from far away, levers can be used to lift enormous loads with ease. The object being moved by the lever is often called the load, or output force, while the force applied to the lever is called the effort, or input force. Crowbars are a commonly-used lever that help workers and carpenters easily extract nails from wood.
An object that tapers to a thin edge and forces a substance apart. It can be used to split things apart, such as an ax, or to hold things, such as a doorstop. Engineers design modern cars and jets using the principle of a wedge to help them cut through the air by including a pointed wedge at the front.
Composed of a circular wheel directly connected to a circular shaft or axle, this device rotates around the common axis and has the ability to increase a rotational force instead of a linear force. Engineers commonly refer to a rotational force as torque and use this simple machine to design and create the steering wheel, jet engine, mechanical gears, and even doorknobs.
A flat, sloping surface that is used for raising or moving heavy objects from one place to another. Inclined planes are used to lift loads that would otherwise be too heavy to lift straight up. The angle or the steepness of the inclined plane determines how much effort is required to move an object. The steeper the angle, the more effort is required. We see inclined planes used in ramps and switchback roads.
The simple machines used by ancient engineers to construct the pyramids in Egypt and the Colosseum in Rome are the same ones used by engineers today to build roller-coasters, skyscrapers and bridges in our modern world. We encounter simple machines in our everyday lives in devices like crowbars, wheelbarrows and highway ramps.
These simple machines leverage the unique phenomenon of mechanical advantage of the design and then engineers combine multiple simple machines to create more advanced tools like cars, bicycles, medical devices and 3D printers.
Check out the resources below filled with various sensemaking tasks grounded in exploring everyday phenomena through the use of simple machines!
Simple Machines Curricula
Grades K-2
- An Introduction to Inclined Planes An Introduction to Inclined Planes

Students are introduced to the concept of simple tools and how they can make difficult or impossible tasks easier. They begin by investigating the properties of inclined planes and how implementing them can reduce the force necessary to lift objects off the ground.
- The Benefits of Inclined Planes: Heave Ho! The Benefits of Inclined Planes: Heave Ho!

Why does setting up an inclined plane on the back of a truck make it easier to load and unload? What's the difference between dragging an object up a slope versus lifting an object straight into the air? Have students learn about the engineering behind the practicalities of inclined planes.
Grades 3-5
- The Power of Mechanical Advantage The Power of Mechanical Advantage

Students learn about the mechanical advantage offered by pulleys in an interactive and game-like manner. Using a LEGO® MINDSTORMS® robotics platform and common hardware items, students build a mechanized elevator system.
- Solid Rock to Building Block Solid Rock to Building Block

Students continue their pyramid building journey, acting as engineers to determine the appropriate wedge tool to best extract rock from a quarry and cut into pyramid blocks. Using sample materials (wax, soap, clay, foam) representing rock types that might be found in a quarry, they test a variety of...
- Slide Right on by Using an Inclined Plane Slide Right on by Using an Inclined Plane

Students explore building a pyramid, learning about the simple machine called an inclined plane. They also learn about another simple machine, the screw, and how it is used as a lifting or fastening device.
- Let's Move It! Let's Move It!

Students explore methods employing simple machines likely used in ancient pyramid building, as well as common modern-day material transportation. They learn about the wheel and axle as a means to transport materials from rock quarry to construction site.
- Simple Machines and Modern Day Engineering Analogies Simple Machines and Modern Day Engineering Analogies

Students apply the mechanical advantages and problem-solving capabilities of six types of simple machines (wedge, wheel and axle, lever, inclined plane, screw, pulley) as they discuss modern structures in the spirit of the engineers and builders of the great pyramids.
- See More
Grades 6-8
- Levers That Lift Levers That Lift

Students are introduced to three of the six simple machines used by many engineers: lever, pulley, and wheel-and-axle. In general, engineers use the lever to magnify the force applied to an object, the pulley to lift heavy loads over a vertical path, and the wheel-and-axle to magnify the torque appl...
- Not So Simple Not So Simple

Students expand upon their understanding of simple machines with an introduction to compound machines. This lesson encourages students to critically think about machine inventions and their role in our lives.
- The Advantage of Machines The Advantage of Machines

In this lesson, students learn about work as defined by physical science and see that work is made easier through the use of simple machines. Already encountering simple machines everyday, students will learn about their widespread uses in improving everyday life.
- Machines and Tools, Part II Machines and Tools, Part II

In this activity, students gain first-hand experience with the mechanical advantage of pulleys. Students are given the challenge of helping save a whale by moving it from an aquarium back to its natural habitat into the ocean.
- A Simple Solution for the Circus A Simple Solution for the Circus

In this activity, students are challenged to design a contraption using simple machines to move a circus elephant into a rail car.
- See More
Grades 9-12
- Simple Machines and the Rube Goldberg Challenge Simple Machines and the Rube Goldberg Challenge
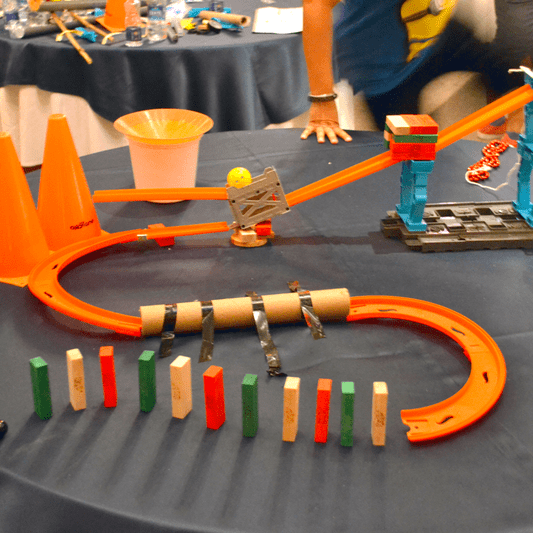
Students research and learn about simple machines and other mechanisms through learning about a Rube Goldberg machine. Student teams design and build their own Rube Goldberg devices that incorporate at least six simple machines. This project is open-ended with much potential for creativity and fun.
- Splash, Pop, Fizz: Rube Goldberg Machines Splash, Pop, Fizz: Rube Goldberg Machines

Refreshed with an understanding of the six simple machines; screw, wedge, pully, incline plane, wheel and axle, and lever, student groups receive materials and an allotted amount of time to act as mechanical engineers to design and create machines that can complete specified tasks.